Infl uences of welding time and amplitude in ultrasonic welding on the strengths of hybrid tape/organo sheet joints with unreinforced intermediate layers
Authors: M. Sc. Max Weihermüller, M. Sc. Vera Austermann, M.Sc. Taiki Hirano, Dr.-Ing. Jens Wipperfürth, Dr. Kai Fischer, Prof. Dr.-Ing. Christian Hopmann
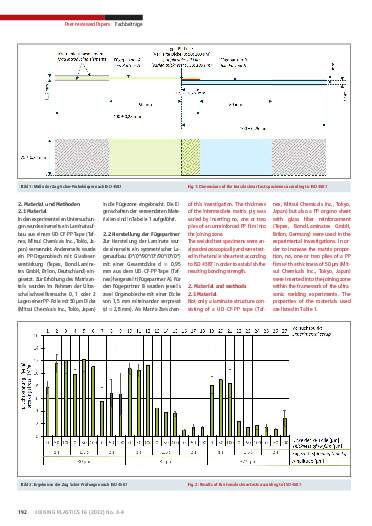
Ultrasonic welding is a very promising technology for the joining of continuous -fiber-reinforced thermoplastics (TP-FRPs) [1]. However, the strengths of joining welds using TP-FRPs with high fi ber volume content may be reduced if not enough matrix material is present in the joining zone [2, 3]. Thus, the effects of the thickness of the intermediate matrix ply on the bonding strength of a joint consisting of a carbon-fiber-reinforced laminate made of tapes and a glass fiber reinforced orango sheet (in each case, with a polypropylene matrix) are investigated within the framework of this article. The thickness of the intermediate matrix ply was varied by inserting no, one or two plies of an unreinforced PP fi lm into the joining zone. The resulting bonding strength in the tensile shear test was analysed according to ISO 4587. Furthermore, the joining zones were analysed microscopically. With a low energy input in the welding process, the results show a clear correlation between the intermediate layer thickness and the attainable breaking strength. It was possible to raise the breaking strength by inserting the intermediate matrix plies. However, a high energy input in the welding process led to the distinct dispelling of fiber and matrix materials from the joining zone and this made it more difficult to establish a clear correlation.
An active subscription enables you to download articles or entire issues as PDF-files. If you already are a subscriber, please login. More information about the subscription